Showing all 4 results
-
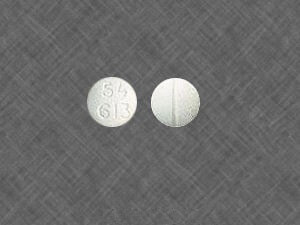
Codeine 15mg
Price: $329.00 Select Pills -
Codeine 300/30mg
Price: $359.00 Select Pills -
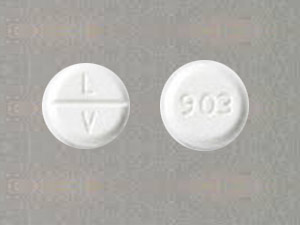
Codeine 30mg
Price: $329.00 Select Pills -
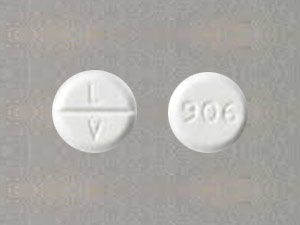
Codeine 60mg
Price: $409.00 Select Pills
What is Codeine?
Codeine is an opioid pain medicine that helps treat Cough and mild to moderately severe pain. It is related to a class of drugs which is known as opioid analgesics. This drug works in the brain to change how your body feels and responds to pain.
Codeine is also available as a brand-name drug codeine sulfate. It is available in pharmacies over the counter (OTC) in many countries, including the UK, South Africa, Ireland, France, and Australia. You can also buy codeine online without a prescription. If you want to order codeine online, make sure to buy it from a trusted online pharmacy.
BUY IT ONLINE WITHOUT A PRESCRIPTION
What are the uses of codeine?
Codeine helps treat mild to moderate pain. This medicine also helps treat cold and flu symptoms if combined with other drugs. Codeine helps treat pain by changing the way the brain and nervous system respond to pain.
How to use codeine?
Take codeine as directed by your doctor. Follow all the directions provided on your prescription label carefully. This medicine can slow or stop your breathing. Your doctor may suggest using this drug alone or with other medications.
Codeine comes in the form of a tablet, a capsule, and a solution or liquid. Take codeine every 4 to 6 hours as needed.
The dosage depends on your medical condition and response to treatment. Do not use codeine in larger amounts or for longer than prescribed. Tell your doctor if the drug seems to stop working as well in relieving your pain.
This drug may be habit-forming, even at regular doses. Therefore, do not share this drug with anyone, especially someone with a history of drug abuse or addiction.
Take this drug with food or milk if it upsets your stomach.
Never stop using codeine suddenly after long-term use, or you could have unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. The withdrawal symptoms include restlessness, mental or mood changes such as trouble sleeping, anxiety, thoughts of suicide, runny nose, watering eyes, sweating, diarrhea, muscle aches, or sudden behavior changes. Ask your doctor how to stop using this medicine safely.
An overdose of this drug can be fatal, especially in a child or other person using the drug without a prescription. The symptoms of an overdose include severe muscle weakness, cold and clammy skin, pinpoint pupils, very slow breathing, extreme drowsiness, or coma.
Dosage
Usual Adult Dose for Pain:
The initial dose of this drug is 15 to 60 mg orally up to every 4 hours as needed.
The maximum dose of this drug is 360 mg in 24 hours.
It is unknown if this drug is safe and effective in children younger than 12 years of age.
Dosage forms and strengths
15 mg tablet: It is a white, biconvex tablet scored on one side, with “15” imprinted on the scored side and an identification number “54 613” imprinted on the other side.
30 mg tablet: It is a white, biconvex tablet scored on one side, with “30” imprinted on the scored side and an identification number “54 783” imprinted on the other side.
60 mg tablet: It is a white, biconvex tablet scored on one side, with “60” imprinted on the scored side and an identification number “54 412” imprinted on the other side.
What to know before taking codeine?
Do not use codeine if you are allergic to it, or if you have:
- a blockage in your stomach or intestines
- severe asthma or breathing problems
- frequent asthma attacks or hyperventilation
To make sure codeine is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have ever had:
- liver disease
- kidney disease
- underactive thyroid
- blockage in your stomach or intestines
- a gallbladder or pancreas disorder
- enlarged prostate, urination problems
- mental illness, drug or alcohol addiction
- low blood pressure
- a head injury or brain tumor
- adrenal gland disorder or Addison’s disease
- breathing disorders such as sleep apnea, asthma, or COPD
Some drugs can interact with codeine and cause a severe condition known as serotonin syndrome. Tell your doctor if you also take:
- stimulant medicine
- herbal products
- medicine for depression or mental illness
- medicine for Parkinson’s disease
- drugs for migraine headaches, serious infections, or prevention of nausea and vomiting
Do not take codeine if you are pregnant. Doing so can make your baby dependent on the drug, causing life-threatening withdrawal symptoms in the baby after it is born.
Do not breastfeed while taking this drug because it can pass into breast milk. It may cause drowsiness, breathing problems, or death in a nursing baby.
What are the side effects of codeine?
The common side effects of codeine include:
- constipation
- sweating
- feeling dizzy or drowsy
- nausea, vomiting, stomach pain
- mild itching or rash
Serious side effects
- noisy breathing, sighing, shallow breathing, or breathing that stops during sleep
- a slow heart rate or weak pulse
- problems with urination
- confusion, agitation, hallucinations, unusual thoughts, or behavior
- feelings of extreme happiness or sadness
- seizure or convulsions
- a light-headed feeling
- low cortisol levels- nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, dizziness, worsening tiredness, or weakness
Narcotic medicines like codeine can slow your breathing which may lead to death.
If you notice any serious side effects such as fainting or seizure, get medical help immediately.
What to avoid while using codeine?
You may have withdrawal symptoms or breathing problems if you start or stop taking certain other medicines. Before taking this drug, tell your doctor if you also use the following medications:
- an antibiotic, antifungal medication
- heart or blood pressure medication
- seizure medication
- medicine to treat HIV or hepatitis C
Taking this medicine with other products that also cause drowsiness or breathing problems may increase severe side effects. The side effects include slow or shallow breathing, extreme drowsiness, or dizziness.
Tell your doctor if you also use the following drugs:
- cold or allergy medicines
- bronchodilator asthma/COPD medication, or a diuretic
medication for motion sickness, irritable bowel syndrome, or overactive bladder - narcotic drugs such as opioid pain medicine or prescription cough medicine
- sedatives which include diazepam, alprazolam, lorazepam, Xanax, Klonopin, Versed, etc
- sleeping pills, muscle relaxers, medicine to treat mood disorders or mental illness
- drugs that affect serotonin levels in your body- a stimulant or medications for depression
- medicines for Parkinson’s disease, migraine headaches, serious infections, or nausea and vomiting
Some medicines can affect the removal of codeine from your body, which may affect how codeine works.
Examples of these drugs include:
- azole antifungals such as ketoconazole
- bupropion
- fluoxetine
- macrolide antibiotics such as erythromycin
- HIV medications such as ritonavir
- paroxetine
- quinidine
- rifamycins such as rifabutin or rifampin
- certain drugs which help treat seizures such as carbamazepine, and phenytoin